Renewable energy sector in India has witnessed significant strides in the past few years. Apart from being a sustainable alternative to polluting fossil fuels, renewable energy can satisfy the country’s energy demand, while bringing down the power cost. Let’s look at the key challenges and opportunities in the segment
Indian power sector is witnessing substantial activity in order to meet the increasing energy needs backed the country’s industrial and infrastructure growth and increased manufacturing activity. With modernization, there is a constant uptick in demand for power capacity to sustain lifestyles. To meet this demand, moving towards renewable and clean sources of energy are at the top of the national agenda. In fact, India is running one of the largest and most ambitious renewable capacity expansion programs in the world.
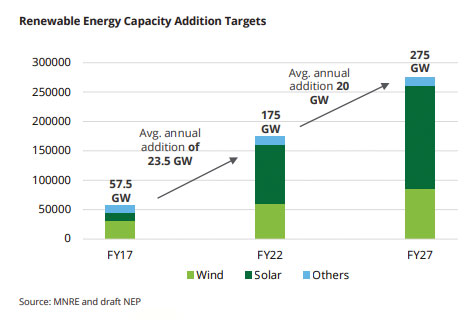
India has set a target of installing 175 GW of renewable generation by 2022, comprising 100 GW solar, 60 GW wind and 15 GW of other forms of renewable generation. Power Minister R K Singh, in October, showed confidence that India is on the right track to achieve this target.
“Today, we have established 83 GW clean energy. About 29 GW of renewable energy is under installation. That makes it 112GW and under about 30GW is under bid. So that makes the 175GW of renewables. I am very confident that we would make it to 175GW of renewables by 2022,” Singh said.
Given government’s focus, India renewable energy sector is attracting foreign and domestic investors. As per industry estimates, India’s renewable energy sector is expected to attract investments of up to $80 billion in the next four years.
New programs such as PM-KUSUM, solar rooftop phase-2, development of Ultra Mega Renewable Energy Power Parks (UMREPPs) are slated to give a further thrust to renewable energy sector in India.
Solar power at the forefront
 India has made tremendous progress in use of solar energy in the recent years. Solar power generation is likely to outweigh other sources, including wind, small hydro, biomass, waste to energy by 2022. The advantage for India is that it is one of the best recipients of solar energy courtesy its location on solar belt. Plus, the subsidies and incentives provided by the Government and Jawaharlal Nehru National Solar Mission (JNNSM) since 2010 have contributed immensely in the adoption of solar energy.
India has made tremendous progress in use of solar energy in the recent years. Solar power generation is likely to outweigh other sources, including wind, small hydro, biomass, waste to energy by 2022. The advantage for India is that it is one of the best recipients of solar energy courtesy its location on solar belt. Plus, the subsidies and incentives provided by the Government and Jawaharlal Nehru National Solar Mission (JNNSM) since 2010 have contributed immensely in the adoption of solar energy.
According to the findings of Mercom India Research, installations in the Indian solar market rose by 36% year-on-year during third quarter of calendar year 2019, reaching 2,170 Mw from 1,592 Mw a year ago. Compared to the second quarter of 2019, installations are up by 44%.
Key challenges
Currently, key issues affecting growth of renewable market is low investor sentiment due to delayed or non-payment by discoms to clean energy developers. As of July 2019, distribution companies across India owed renewable power producers Rs 9,736 crore, according to CEA data. Around three-quarters of that were owed by four southern states — Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Telangana and Karnataka. Ambiguity over goods and services tax (GST) on solar equipment is also hampering the growth. Other major deterrents include safeguard duty on imported solar panels and lack of funding.
The issue of storage of renewable energies also needs to be addressed. Energy storage technologies provide flexibility in the use of electricity, for both centralised and decentralised supply provisions. Advanced battery technologies could enable rapid deployment of rooftop solar installations, which is currently impacted by the high cost of energy storage solutions.
Government is also exhibiting interest in energy storage and pursuing innovative solutions. “Development of storage systems is necessary in order to ensure 24×7 power supply using RE sources like solar and wind. We are committed for the growth and development of the storage systems such as Lithium-ion batteries, pumped Hydro and Hydrogen. We shall be technology neutral in this and allow the market to decide the appropriate systems in various performances depending on markets,” said Power Minister R K Singh. As per the findings of Council on Energy, Environment and Water, the energy storage market for off-grid renewables in India will be worth
Rs 130 billion in 2022.
Land for renewable projects is another key challenge in India as the high cost reflects on the price of electricity. To address this challenge, government is looking at barren lands for building renewable projects so as to avoid any clash with growing need for agricultural production.
The Road Ahead
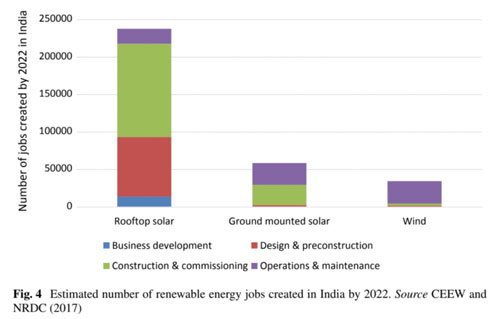
Renewable energy sector in the country has witnessed significant strides in the last decade. Apart from being a sustainable alternative to polluting fossil fuels, renewable energy can satisfy the country’s energy demand, while bringing down the cost. As per estimates, replacing coal plants with renewable sources is expected to save India Rs 54,000 crore annually due to reduced power costs. Further, renewable energy sector will also favourably impact employment generation. According to the International Labour Organization, Indian renewables sector will create around 330,000 new jobs by 2022 and more than 24 million new jobs by 2030.
India is currently targeting to increase the share of renewable energy in the national energy mix to 40% by 2030. The country is evaluating new technologies, such as floating solar, offshore wind, wind–solar hybrid and storage to attain this target. Maximizing India’s renewable energy potential and achieving these ambitious targets is dependent on sufficient technological breakthrough in energy storage in the near future, as well as the affordability factor.
Article by by Shweta Nanda, Assistant Editor, PowerTech Review

